Strong Name Signing Your Assemblies
What is it for?
Strong naming basically helps to make sure that other assemblies can be 100% sure that they are using the correct assembly and they there has been no messing around
In reality, this not a 100% secure process, but it does help in most cases to add a certain amount of safeguard.
And in any case, a lot of applications require it, and if your app is not strong named, then they will not be able to use it.
How to add strong name to my assemblies
The process is fairly straight forward, (surprisingly so), and you don’t need to worry about Visual Studio until the end.
- On your system locate the file called
sn.exe, (in my case, I had a few of them, the actual version does not matter, but I chose the latest one I have). - Open a command line with Administrator privilege, (might not be required, but I don’t know how secure your system is).
- Navigate to the folder where that exe is located.
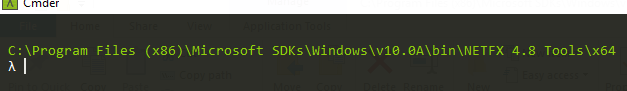
- Create a key … any key, just make sure you give it a name that matters to your application
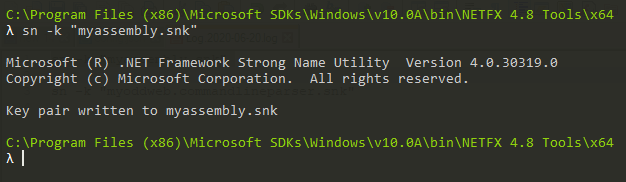
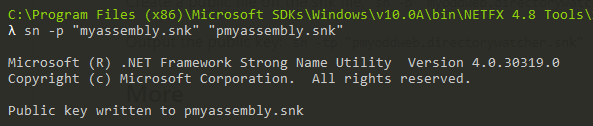
- Now get the public key for your application
sn -p "myassembly.snk" "pmyassembly.snk"
I added the letter “P” in front of my strong name key … so I know it is the public key … but really, you can call it whatever you want.
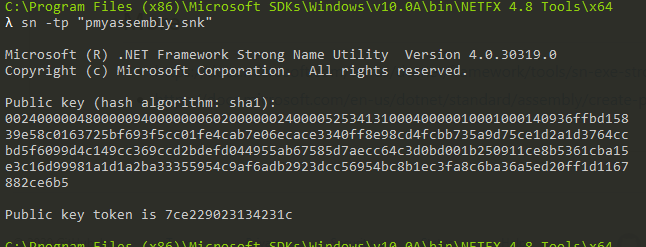
- You might also want your public key as a string value
sn -tp "pmyassembly.snk"
- Or you can be one of the cool kids and output to your clipboard
sn -tp "pmyassembly.snk" |clip
And then you can paste it where ever - I really suggest that you move the file, (with a better name), to your directory
- Then fire up your visual studio project
- Look for the properties
- Select the signing tool
- And check “sign the Assembly”
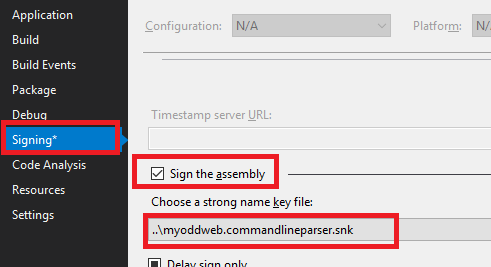
- Annoyingly enough, Visual Studio will move the file where it feels it should be, (next to the
*.csproj), if you really want it somewhere else, just edit the*.csprojfile and change the location yourself. Or don’t, whatever. - Build it
- Ship it
What about my Unit tests?
If you have unit tests running and you are testing internal classes … then you will need to add the public key, (see above), to your InternalsVisibleTo( … )
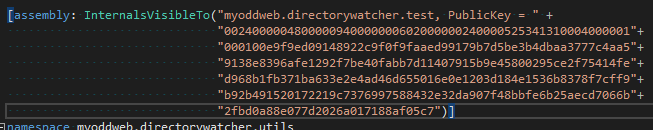
At the end of the day, this is pretty much what consumers of your assembly will do.
What info must I share?
- Your
*.snkfile - Your public key text value
Remember, this is just to verify the identity of your file, not to do some NSA proof securing of some sort.
You want to share the information so others can use it in their own projects.
Recent Comments